2024
Publication in Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry
 09. September 2024
09. September 2024
Publication entitled "Anticancer dinuclear Ir(III) complex activates Nrf2 and interferes with NAD(H) in cancer cells" (authors: E. Řezníčková, O. Bárta, D. Milde, V. Kryštof, P. Štarha) has been published in Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry.
Dinuclear Ir(III) complex 1 exhibits low micromolar cytotoxic activity (GI50 = 1.7–3.0 μM) and outperformed its mononuclear analogue (2; GI50 > 40.0 μM). Compound 1 upregulated the Keap1/Nrf2 oxidative stress-protective pathway in the treated MV4‐11 acute myeloid leukemia cells. In connection with the redox-mediated mode of action of 1, its NADH-oxidizing activity was detected in solution (1H NMR), while NAD+ remained intact (with formate as a hydride source). Following the results of in-solution experiments, NAD(H) concentration was assessed in 1-treated MV4‐11 cancer cells. Besides the intracellular NADH oxidation in the presence of 1, the induced oxidative stress also led to a decrease of NAD+, resulting in depletion of both NAD+/NADH coenzymes. The discussed findings provide new insight into the biochemical effects of catalytic anticancer compounds that induce cell death via a redox-mediated mode of action.
Student Publication in RSC Advances
 04. September 2024
04. September 2024
Publication entitled „Synthesis, structural and magnetic properties of cobalt(II) complexes with pyridine-based macrocyclic ligand containing two pyridine pendant arms" (authors: E. Zahradníková, C. Pichon, C. Duhayon, J. P. Sutter, P. Halaš, B. Drahoš) has been published in the chemistry journal RSC Advances.
The student publication was focused on the research and tuning of the magnetic anisotropy for a series of cobalt(II) complexes with a 17-membered pyridine macrocyclic ligand with two methylpyridine pendant arms and one coordinated (pseudo)halido-coligand. The work followed the previous research with a structurally similar macrocyclic system where an interesting magnetic behavior was observed within the analogous series. The performed magnetic studies were additionally supported by theoretical CASSCF calculations and a positive value of the axial zero-field splitting parameter D was found for all complexes, and one of the complexes showed behavior typical for compounds referred to as field-induced single-molecule magnets.
Student Publication in Dalton Transactions
 22. May 2024
22. May 2024
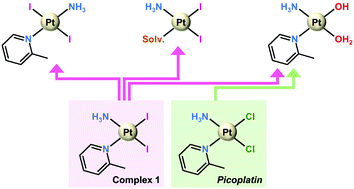
Publication entitled "Picoplatin binding to proteins: X-ray structures and mass spectrometry data on the adducts with lysozyme and ribonuclease A" (authors: G. Ferraro, T. Lyčková, L. Massai, P. Štarha, L. Messori, A. Merlino) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this article, the reactivity of the Pt(II) anticancer compound picoplatin (cis-ammine-dichlorido-(2-methylpyridine)platinum(II) complex) with the model proteins hen egg white lysozyme (HEWL) and bovine pancreatic ribonuclease (RNase A) was investigated by electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry (MS) and X-ray crystallography. MS data show binding of Pt to both proteins, with fragments retaining the 2-methylpyridine ligand. Crystallography identifies different binding sites on the two proteins, highlighting a different behaviour of picoplatin in the absence or presence of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The data suggest that the presence of DMSO favours the loss of 2-methylpyridine and alters the ability of the Pt compound to bind to the proteins. This study provides important insights into the pharmacological profile of picoplatin and supports the conclusion that coordinating solvents should not be used to evaluate the biological activities of Pt-based drugs.
2023
Student Publication in Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers
 13. December 2023
13. December 2023
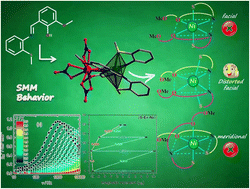
Publication entitled „2-Formylphenoxyacetic acid Schiff bases: a promising ligand scaffold for readily available trigonal prismatic Co(II) single-ion magnets" (authors: Kamil Kotrle, Ivan Nemec, Peter Antal, Kamila Petrželová, Erik Čižmár, Radovan Herchel) has been published in the chemistry journal Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers.
This work is focused on the preparation and characterization of a series of cobalt complexes with Schiff base ligands that tend to adopt the shape of a trigonal prism. These complexes were synthesized, structurally characterized, and subsequently subjected to magnetic measurements using magnetometry and EPR spectroscopy. It was found that the complexes exhibit single-molecule magnet properties in the presence of a magnetic field. One of the complexes was magnetically diluted, revealing single-molecule magnet properties even in a zero field. These properties were further investigated through theoretical calculations.
Student Publication in Dalton Transactions
 12. December 2023
12. December 2023
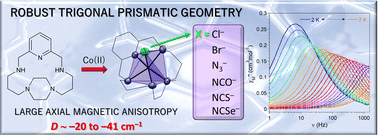
Publication entitled „Trigonal prismatic coordination geometry imparted by a macrocyclic ligand: an approach to large axial magnetic anisotropy for Co(II)" (authors: E. Zahradníková, J. P. Sutter, P. Halaš, B. Drahoš ) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this work, we were dealing with the preparation of cobalt(II) complexes with 17-membered pyridine-piperazine macrocyclic ligand with atypical shape of trigonal prism coordination polyhedron. The ligand is coordinated by all five N-donor atoms and the last position is occupied by monovalent coligand – halide or pseudohalide. A negative value of the D-parameter describing the magnetic anisotropy in the range -20 to -41 cm-1 was found for all complexes and the magnetic behaviour was investigated using theoretical calculations and magnetochemical measurements. Five field-induced single-molecule magnets were prepared and the magnetostructural correlations were investigated.
Publication in Coordination Chemistry Reviews
 12. December 2023
12. December 2023
Publication entitled "Platinum(IV) and platinum(II) anticancer complexes with biologically active releasable ligands" (authors: P. Štarha, R. Křikavová) has been published in Coordination Chemistry Reviews.
In this review article, we focused on a comprehensive overview of the structural types of multi-targeted Pt(IV) complexes, and they were categorized according to various criteria - a parent Pt(II) complex, a number and type of bioactive ligands, a type of second (innocent) axial ligand, and nuclearity. For the first time, we also reviewed multi-targeted Pt(II) complexes releasing cytotoxic Pt(II) species and bioactive ligand(s) as well, which also allowed a critical comparison of the two structural types. Special attention is paid to the discussion of the solution behaviour, activation and biological activity of the reviewed types of Pt complexes. Relevant comparison of these crucial features should be beneficial for future development of these pharmacologically highly perspective compounds.
Student Publication in Magnetochemistry
 28. November 2023
28. November 2023
Publication entitled "Honey-like Odor Meets Single-Ion Magnet: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Magnetism of Cobalt(II) Complex with Aromatic Trans-Cinnamic Acid" (authors: P. Halaš, I. Nemec, R. Herchel) has been published in the chemistry journal Magnetochemistry.
This work presents synthesis and physicochemical characterization of Co(II) complex containing neocuproine and cinnamic acid as ligands. Coordination polyhedron assumes deformed octahedral shape, mostly due to the unusual bidentate coordination mode of the cinnamate anion. Complex exhibits slow relaxation of magnetization under applied field and axial type of magnetic anisotropy with parameter D = 53.2 cm−1. Analysis of magnetic properties was supported by CASSCF/NEVPT2 calculations.
Student Publication in Inorganic Chemistry
 07. November 2023
07. November 2023
Publication entitled „Theoretical Magnetic Relaxation and Spin–Phonon Coupling Study in a Series of Molecular Engineering Designed Bridged Dysprosocenium Analogues" (authors: Kamil Kotrle, Mihail Atanasov, Frank Neese, Radovan Herchel ) has been published in the chemistry journal Inorganic Chemistry.
The work is based on theoretical calculations focused on the magnetic properties of a series of dysprosocenium-type complexes. For these complexes, structure optimizations were performed, an analysis of their vibrational frequencies was conducted, and subsequently, their energy barriers Ueff were studied using methods based on CASSCF calculations. Furthermore, spin-phonon coupling was investigated, where a new method based on comparing the influence of molecular vibrations on the energy barrier was developed and compared to the already used method, which relies on crystal field parameters. The study of these substances revealed interesting structural correlations that could potentially be utilized in the design of single-molecule magnets with high blocking temperatures.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 20. September 2023
20. September 2023
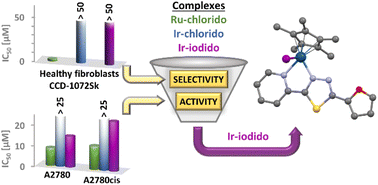
Publication entitled „Impact of the central atom and halido ligand on the structure, antiproliferative activity and selectivity of half-sandwich Ru(II) and Ir(III) complexes with a 1,3,4-thiadiazole-based ligand" (authors: R. Křikavová, M. Romanovová, Z. Jendželovská, M. Majerník, L. Masaryk, P. Zoufalý, D. Milde, J. Moncol, R. Herchel, R. Jendželovský, I. Nemec) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
Half-sandwich Ru(II) and Ir(III) complexes with a thiadiazole-based ligand L1 (2-(furan-2-yl)-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1,3, 4-thiadiazole) were synthesized and characterized by different analytical methods. The structures of the molecules were analysed and interpreted by computational methods (DFT and QT-AIM). The complexes showed the ability to oxidize NADH to NAD+, with the Ir(III) complexes exhibiting higher catalytic activity compared to their Ru(II) analogues. The results of in vitro testing of antiproliferative activity showed that Ir(III) complexes had no effect on healthy human fibroblasts, demonstrating their selectivity. In contrast, the complexes showed inhibitory effects on the metabolic and proliferative activity of cancer cells.
Our student received a poster award at the conference 75. Sjezd chemiků
Publication in New Journal of Chemistry
 22. August 2023
22. August 2023
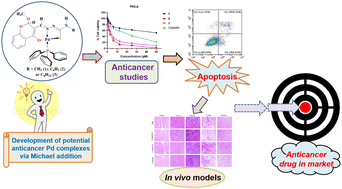
Publication entitled "Michael addition-driven synthesis of cytotoxic palladium(II) complexes from chromone thiosemicarbazones: investigation of anticancer activity through in vitro and in vivo studies" (authors: J. Haribabu, N. Balakrishnan, S. Swaminathan, D.P. Dorairaj, M. Azam, M.K.M. Subarkhan, Y.-L. Chang, S.C.N. Hsu, P. Štarha, R. Karvembu) has been published in the chemistry journal New Journal of Chemistry.
A series of Pd(II) complexes with tridentate chromone-based thiosemicarbazones (TSCs) was prepared, characterized by appropriate analytical techniques and studied for their anticancer activity. The TSC ligands used in the syntheses were subjected to in situ Michael addition. Two complexes exhibited low-micromolar antiproliferative activity against HeLa cervical cancer cells. The complexes were also studied for their mechanism of action and tested for their toxicity in vivo. In contrast to tissue-damaging cisplatin, normal cell and tissue architecture was observed in mice treated with Pd(II) complexes.
Student Publication in Dalton Transactions
 18. August 2023
18. August 2023
Publication entitled „Lanthanoid coordination prompts unusually distorted pseudo-octahedral NiII coordination in heterodinuclear Ni–Ln complexes: synthesis, structure and understanding of magnetic behaviour through experiment and computation" (authors: Biswarup Dutta; Thierry Guizouarn; Fabrice Pointillart; Kamil Kotrle; Radovan Herchel; Debashis Ray) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this paper, a series of complexes [NiLn(L)2(NO3)3] (Ln = Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Yb, Y) with a Schiff base ligand were prepared. These complexes underwent characterization through X-ray structural studies and other physical-chemical methods. Additionally, their magnetic properties were explored using both experimental and theoretical methods. The results indicated that the complexes of Dy, Er, and Yb exhibit characteristics of field-induced single-molecule magnets.
Student Publication in Dalton Transactions
 13. June 2023
13. June 2023
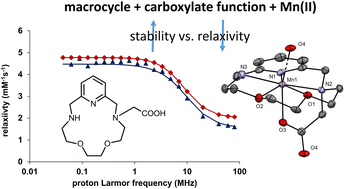
Publication entitled „A seven-coordinate Mn(ii) complex with a pyridine-based 15-membered macrocyclic ligand containing one acetate pendant arm: structure, stability and relaxation properties" (authors: M. Pražáková, D. Ndiaye, É. Tóth, B. Drahoš) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this work, a new hexadentate macrocyclic ligand containing one acetate pendant arm was synthesized. Its manganese complex was characterized in the context of its use as a potential MRI contrast agent. Using X-ray analysis, coordination number seven was confirmed, and in aqueous solution the seventh coordination site was occupied by a water molecule. Furthermore, advanced solution measurements (potentiometry, 17O NMR and 1H NMRD, relaxometry) were performed, which showed very good thermodynamic stability of the manganate complex, its relatively small kinetic inertness and MRI efficiency of the complex (expressed by so-called relaxivity, r1 = 2.45 mM−1 s−1 at 20 MHz, 25 °C), which corresponded to the presence of one coordinated water molecule. Compared to the manganate complex of the parent macrocycle without the acetate arm, this system represents a substantial improvement in thermodynamic and kinetic stability but a decrease in its efficiency/relaxivity.
Patent granted
 09. June 2023
09. June 2023
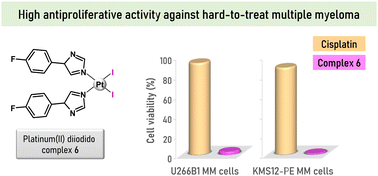
Czech patent "Komplexy platiny pro léčbu mnohočetného myelomu" was granted to the coauthors from the Department of Inorganic Chemistry.
The collaboration of the Department of Inorganic Chemistry (Faculty of Science, UP) and the Department of Clinical and Molecular Pathology (Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, UP) has led to the development of a series of diiodoplatinum(II) complexes with simple imidazole derivatives, which have been shown to be highly effective against multiple myeloma cell lines, known to be a very difficult to treat type of cancer. The compounds studied and their use for the treatment of multiple myeloma are the subject of patent protection by the Industrial Property Office of the Czech Republic (patent CZ 309542 B6).

Student Publication in Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers
 02. June 2023
02. June 2023
Publication entitled "Anti-myeloma pro-apoptotic Pt(II) diiodido complexes" (authors: L. Masaryk, D. Weiser Drozdková, K. Słoczyńska, J. Moncol’, D. Milde, R. Křikavová, J. Popiół, E. Pękala, K. Ondrušková, I. Nemec, K. Smešný Trtková, P. Štarha) has been published in the chemistry journal Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers.
Diiodidoplatinum(II) complexes cis-[PtI2(Ln)2] (1–7) with imidazole derivatives (Ln) were considerably effective against multiple myeloma cell lines U266B1 and KMS12-PE. The leading compound 6 extraordinarily reduced viability of myeloma cells and exceeded the conventional anticancer drug cisplatin. Complex 6 also displayed markedly lower activity in the HS-5 stromal fibroblast cells than in myeloma cells, pointing out its pharmocologically prospective selectivity towards the cancer cells. No caspase 3/7 activity was detected in apoptotic myeloma cells treated by 6 indicating a different mechanism of apoptosis action from cisplatin. This work demonstrates that simple non-classical platinum(II) complexes represent a new perspective for a monotherapy of hard-to-treat multiple myeloma.
Our student received the French Barrande Fellowship
 09. May 2023
09. May 2023
PhD student in Inorganic Chemistry Mgr. Eva Zahradníková succeeded in the Barrande Fellowships 2023 program and received a scholarship that will finance her internship abroad in France. Congratulations!
Student Publication in Crystal, Growth & Design
 02. March 2023
02. March 2023
Publication entitled "Variation of Spin-Transition Temperature in the Iron(III) Complex Induced by Different Compositions of the Crystallization Solvent" (authors: I. Nemec, L. Kotásková, R. Herchel) has been published in the chemistry journal Crystal, Growth & Design.
In this work, we thoroughly investigated the relationship between the crystallization rate and the critical temperature of spin crossover for an iron(III) complex exhibiting spin crossover and thermal hysteresis. By utilizing X-ray diffraction, we discovered that the critical temperature of spin crossover (T1/2) is correlated with the crystallization time. Longer crystallization times resulted in crystals with lower T1/2 values, while shorter crystallization times resulted in crystals with higher T1/2 values. The difference between the highest and lowest T1/2 values observed can be as much as 50K.
Excursion of the Department of Inorganic Chemistry
23. January 2023
For the pupils of the Křižná Primary School in Valašské Meziříčí and the Church Grammar School of the German Order, we organized interesting excursions at the Department of Inorganic Chemistry.
Student publication in Inorganica Chimica Acta
 22. January 2023
22. January 2023
Publication entitled "Antibacterial study on nickel and copper dicarboxylate complexes" (authors: I. Loubalová, E. Zahradníková, L. Masaryk, I. Nemec, L. Hochvaldová, A. Panáček, L. Kvítek, R. Večeřová, M. Swiatkowski, P. Kopel) has been published in the chemistry journal Inorganica Chimica Acta.
Series of nickel and copper complexes with dicarboxylic acids (2,2 '-thiodiacetic acid, 3,3 '-thiodipropionic acid, 3,3 '-dithiodipropionic acid, and fumaric acid) and N-donor ligands (1,2-diaminopropane, 1,3-diaminopropane, 1,10-phenanthroline and N,N,N ',N '',N ''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine) were synthesized and characterized using elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. These coordination compounds were tested for their antibacterial activities in vitro. The complexes demonstrated moderated antibacterial ac-tivity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and could potentially be applied to treat skin wounds..
2022
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 06. December 2022
06. December 2022
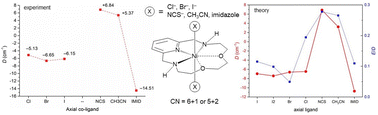
Publication entitled "Effective tuning of magnetic anisotropy in distorted pentagonal bipyramidal Ni(ii) complexes via substitution of axial coligands" (authors: B. Drahoš, R. Herchel) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this paper, a series of Ni(II) complexes with pyridine-based macrocyclic ligand L with general formula [Ni(L)(X)2]0/2+ (X = Br− (1), I− (2), CH3CN (3), NCS− (4), imidazole (5)) was prepared and thoroughly investigated. X-ray molecular structures confirmed pentagonal bipyramidal geometry for all studied complexes with a strong Jahn–Teller distortion in the pentagonal equatorial plane. Direct current magnetic measurements revealed a strong easy-axis type of magnetic anisotropy which remains not affected in the halogenido series Cl− → Br− → I−, but which increases in the series with N-axial ligands in order CH3CN → NCS− → imidazole. This trend was explained with help of extensive theoretical calculations which confirmed a significant positive effect on magnetic anisotropy of changing axial ligand field as well as a negative effect of equatorial ligand field distortion and pointed to complexity of magnetic anisotropy tuning in pengatonal bipyramidal complexes with not strictly rigid macrocyclic ligand.
Publication in Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers
 20. October 2022
20. October 2022
Publication entitled "Pentacoordinate cobalt(II) single ion magnets with pendant alkyl chains: shall we go for chloride orbromide?" (authors: J. Juráková, J. Dubnická Midlíková, J. Hrubý, A. Kliuikov,V. T. Santana, J. Pavlik, J. Moncoľ, E. Čižmár, M. Orlita, I. Mohelský, P. Neugebauer, D. Gentili, M. Cavallini, I. Šalitroš) has been published in the chemistry journal Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers.
The publication deals with the preparation, structural and magnetic studies of four pentacoordinate Co(II) single molecule magnets. Entitled coordination compounds contain Cl- or Br- terminal ligands along with tridentate bis(benzimidazole)pyridine aromatic lignads decorated with n-alkyl chains. The comprehensive analysis of magnetic properties was focused on the diferences in the slow relaxation of magnetisation of investigated single molecule magnets. The investigated chlorido complexes exhibit the longer relaxation mediated via different relaxation mechanisms comparing to the isostructural bromido complexes. Those important finding will be very useful in the case of further molecular design of the novel single molecule magnets.
Student publication in Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers
 27. July 2022
27. July 2022
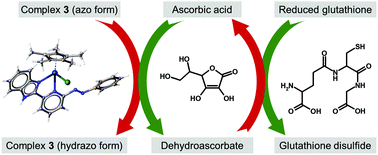
Publication entitled "Anticancer half-sandwich Ir(III) complex and its interaction with various biomolecules and their mixtures - a case study with ascorbic acid" (authors: L. Masaryk, J. Orvoš, K. Słoczyńska, R. Herchel, J. Moncol, D. Milde, P. Halaš, R. Křikavová, P. Koczurkiewicz-Adamczyk, E. Pękala, R. Fischer, I. Šalitroš, I. Nemec, P. Štarha) has been published in the chemistry journal Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers.
Cytotoxic half-sandwich complex [Ir(η5-Cp*)Cl(L2)]PF6 (3) with 2‑pyridin-benzimidazole-based azo ligand was studied in the presence of various extra- and intracellular biologically relevant molecules. For the first time, the mixtures of 3 with ascorbic acid (ASA) and its combinations with reduced glutathione (GSH) and/or reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) were studied. 3 undergoes the azo bond reduction when mixed with NADH or ASA, but only ASA is recovered in the presence of GSH.
Student publication in Dalton Transactions
 23. June 2022
23. June 2022
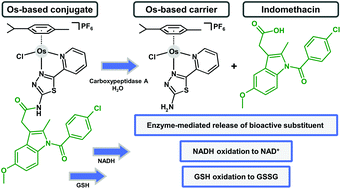
Publication entitled "Stability of a half-sandwich Os(ii) complex with indomethacin-functionalized ligand in the presence of carboxypeptidase A" (authors: L. Masaryk, D. Muthná, P. Halaš, P. Zoufalý, E. Peterová, R. Havelek, B. Drahoš, D. Milde, A. Mrkvicová, P. Štarha) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In the presence of carboxypeptidase, the hydrolytically stable complex [Os(η6-pcym)(L2)Cl]PF6 (2) partially released the bioactive substituent indomethacin, bound through the amide bond to the chelating 2-(1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)pyridine-based moiety of L2. Stability in the presence of other relevant biomolecules (GSH, NADH, GMP) and cancer cell viability were also studied.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 17. May 2022
17. May 2022
Publication entitled "Impact of counter anions on spin-state switching of manganese(III) complexes containing an azobenzene ligand" (authors: S. Ghosh, S. Bagchi, S. Kamilya, S. Mehta, D. Sarkar, R. Herchel, A. Mondal) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
A series of four mononuclear manganese(III) complexes coordinated with photo-active hexadentate azobenzene ligand, [Mn(5azo-sal2-323)](X) (X– = Cl, BF4, ClO4, PF6), were prepared. The impact of various counter anions on the stabilization and switching of the spin state of the manganese(III) center was explored through detailed magneto-structural investigation using variable temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction, magnetic, spectroscopic, and spectroelectrochemical studies, along with theoretical calculations.
Student publication in Inorganica Chimica Acta
 30. March 2022
30. March 2022
Publication entitled „ New Pt(II) diiodido complexes containing bidentate 1,3,4-thiadiazole-based ligands: Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity“ (authors: L. Masaryk, P. Zoufalý, K. Słoczyńska, E. Zahradniková, D. Milde, P. Koczurkiewicz-Adamczyk, P. Štarha) has been published in the journal Inorganica Chimica Acta.
Two new cis-diiodidoplatinum(II) complexes involving bidentate 1,3,4-thiadiazole-based ligands interacted effectively with CT-DNA. Within a panel of human cancer cell lines, only the HepG2 and A549 cells were sensitive towards the studied complexes, but their in vitro cytotoxicity was lower than determined for the reference drug cisplatin.
Publication in Analytical Chemistry
 15. March 2022
15. March 2022
Publication entitled „Ratiometric pH-Responsive 19F Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents Based on Hydrazone Switches“ (authors: D. Janasik, K. Jasiński, W. P. Węglarz, I. Nemec, P. Jewula, T. Krawczyk) has been published in the journal Analytical Chemistry.
Student publication in Materials
10. February 2022
Publication entitled "Trigonally distorted hexacoordinate Co(II) Single-Ion Magnets" (authors: I. Nemec, O. F. Fellner, B. Indruchová, R. Herchel) has been published in the journal Materials.
We investigated the crystal structure and magnetism of three Co(II) complexes with neocuproine and carboxylate ligands. We revealed that even by using very simple ligands we can achieve high trigonality of the coordination polyhedron needed for the stabilization of double degenerate ground state and thus, observation of large axial anisotropy.

2021
Student publication in Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications
 21. December 2021
21. December 2021
Publication entitled "Anion-Dependent Synthesis of Cu(II) Complexes with 2-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)-1H-indole: Synthesis, X-Ray Structures, and Radical Scavenging Activity" (authors: P. Halaš, J. Kuchár, R. Herchel ) has been published in the chemistry journal Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications.
This work is dedicated to the synthesis, characterization and radical scavenging activity of two copper(II) complexes containing 2-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-1H-indole and 1,10-phenanthroline as ligands. Special attention is given to the descriptions of crystal structures of tetrazole-based ligand as well as copper(II) complexes. The ability of complexes to scavenge free radicals was confirmed and quantified spectrophotometrically by scavenging of model radical DPPH. In order to elucidate the possible scavenging mechanism, DFT calculations were performed and revealed that the main mechanism is single electron transfer (SET), during which Cu(II) is reduced to Cu(I).

Publication in Materials
21. December 2021
Publication entitled "Utilisation of Carp Skin Post-Production Waste in Binary Films Based on Furcellaran and Chitosan to Obtain Packaging Materials for Storing Blueberries" (authors: M. Janik, E. Jamróz, J. Tkaczewska, L. Juszczak, P. Kulawik, M. Szuwarzyński, K. Khachatryan, P. Kopel) has been published in the journal Materials.
An innovative three-component biopolymer film based on chitosan (CHIT), furcellaran (FUR) and a gelatin hydrolysate from carp skins (Cyprinus carpio) (HGEL) was developed. The structure and morphology were characterised using the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The FT-IR test showed no changes in the matrix after the addition of HGEL, which indicates that the film components were compatible. Based on the obtained AFM results, it was found that the addition of HGEL caused the formation of grooves and cracks on the surface of the film (reduction by ~21%). The addition of HGEL improved the antioxidant activity of the film (improvement by up to 2.318% and 444% of DPPH and FRAP power, respectively). Due to their properties, the tested films were used as active materials in the preservation of American blueberries. In the active films, the blueberries lost mass quickly compared to the synthetic film and were characterised by higher phenol content. The results obtained in this study create the opportunity to use the designed CHIT–FUR films in developing biodegradable packaging materials for food protection, but it is necessary to test their effectiveness on other food products.

Student publication in Polyhedron
 29. November 2021
29. November 2021
Publication entitled "Syntheses and crystal structures of Ni(II) complexes with pyridine-based macrocyclic ligands" (authors: E. Zahradníková, I. Císařová, B. Drahoš) has been published in the chemistry journal Polyhedron.
In this work, three structurally new pyridine-based macrocyclic ligands, two containing one pyridine pendant arm (L1 and L2) and one containing piperazine rings in the macrocyclic scaffold (L3), with an increasing size of the macrocycle from 12-, 14- to 30-membered ring for L1–L3 were synthesized and characterized. A series of three Ni(II) complexes with all these ligands was prepared. Based on the results of X-ray structural analysis, the prepared complexes were found as six-coordinate with octahedral geometry (coordination spheres were completed by solvent molecule(s)). The values of effective magnetic moments, determined by the Evans method in solution, well corresponded to the theoretical spin-only values.
Publication in Materials
19. November 2021
Publication entitled "Active Double-Layered Films Enriched with AgNPs in Great Water Dock Root and Pu-Erh Extracts" (authors: E. Jamróz, A. Cabaj, L. Juszczak, J. Tkaczewska, M. Zimowska, A. Cholewa-Wójcik, P. Krzyściak, P. Kopel) has been published in the journal Materials.
A novel, eco-friendly, and biocompatible method was applied to form silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in great water dock (Lapathi radix) (KB) and pu-erh (Camellia sinensis) (PE) extracts. The surface plasma resonance peak of green synthesized AgNPs at 451.8 nm for AgNPs+KB and 440.8 nm for AgNPs+PE was observed via spectral analysis of UV absorbance. In this study, double-layered biopolymer films (FUR/CHIT+HGEL) with AgNPs incorporated in KB solution (AgNPs+KB) and AgNPs in PE solution (AgNPs+PE), were successfully prepared using the casting method. The SEM, XRD, zeta potential and size analyses confirmed the presence of AgNP in the films. The addition of AgNPs in plant extracts improved antimicrobial and antioxidant activity and thermal stability, whereas WVTR experienced a decrease. The nanocomposite films’ orange-brown colour may aid in the protection of food products against UV rays. The composite films demonstrated antibacterial activity against food-borne pathogens and may offer potential in food packaging applications.

Publication in Dalton Transactions
 20. October 2021
20. October 2021
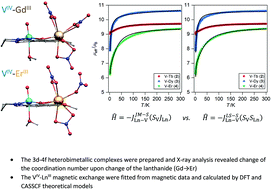
Publication entitled "3d–4f magnetic exchange interactions and anisotropy in a series of heterobimetallic vanadium(iv)–lanthanide(iii) Schiff base complexes" (authors: K. Kotrle, I. Nemec, J. Moncol, E. Čižmár, R. Herchel ) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
A series of new complexes containing vanadium and lanthanides has been prepared, and it was revealed, that two reported complexes are the first single-molecule magnets among this class of V(IV) – Ln(III) compounds. A number of different theoretical methods for determining magnetic exchange in lanthanide containing compounds was utilized and compared in this publication.
Publication in Polymers
 25. August 2021
25. August 2021
Publication entitled "Application of Furcellaran Nanocomposite Film as Packaging of Cheese" (authors: A. Pluta-Kubica, E. Jamróz, G. Khachatryan, A. Florkiewicz, P. Kopel) has been published in the journal Polymers.
There is a serious need to develop and test new biodegradable packaging which could at least partially replace petroleum-based materials. Therefore, the objective of this work was to examine the influence of the recently developed furcellaran nanocomposite film with silver nanoparticles (obtained by an in situ method) on the quality properties of two cheese varieties: a rennet-curd (gouda) and an acid-curd (quark) cheese. The water content, physicochemical properties, microbiological and organoleptic quality of cheese, and migration of silver nanoparticles were examined. The film improved the microbiological quality of cheeses during storage. Consequently, it is worth continuing research for the improvement of this film in order to enable its use in everyday life.
Publication in International Journal of Nanomedicine
25. August 2021
Publication entitled "The Anti-Proliferative Activity of Coordination Compound-Based ZnO Nanoparticles as a Promising Agent Against Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells" (authors: H. Stepankova, M. Swiatkowski, R. Kruszynski, P. Svec, H. Michalkova, V. Smolikova, A. Ridoskova, Z. Splichal, P. Michalek, L. Richtera, P. Kopel, V. Adam, Z. Heger, S. Rex) has been published in the medical journal International Journal of Nanomedicine.
The present study deals with the in vitro evaluation of the potential use of coordination compound-based zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer cells (TNBrCa). Prepared by reacting zinc carboxylates and hexamethylenetetramine, 4 distinct coordination compounds were further subjected to two modes of conversion into ZnO NPs - ultrasonication with oleic acid or heating of pure precursors in an air atmosphere. The resulting ZnO NPs provide distinct morphological features, size, biocompatibility, and selective cytotoxicity toward TNBrCa cells. The crucial properties of ZnO NPs seem to be their morphology, size, and zinc content. The ZnO NPs with the most preferential values of all three properties show great promise for a future potential use in the therapy of TNBrCa.
Publication in Journal of Nanobiotechnology
25. August 2021
Publication entitled " Mutual influence of selenium nanoparticles and FGF2-STAB® on biocompatible properties of collagen/chitosan 3D scaffolds: in vitro and ex ovo evaluation" (authors: J. Muchová, V. Hearnden, L. Michlovská, L. Vištejnová, A. Zavaďáková, K. Šmerková, S. Kočiová, V. Adam, P. Kopel, L. Vojtová) has been published in the biotechnology journal Journal of Nanobiotechnology .
In vitro and ex ovo biocompatibility of naturally based crosslinked freeze-dried 3D porous collagen/chitosan scaffolds, modified with thermostable fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2-STAB(R)), to enhance healing and selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) to provide antibacterial activity, were evaluated.
The scaffolds were further subjected to antimicrobial tests, where an increase in selenium concentration in the collagen/chitosan scaffolds increased the antibacterial activity. This work highlights the antimicrobial ability and biocompatibility of newly developed crosslinked collagen/chitosan scaffolds involving FGF2-STAB(R) and SeNPs. Moreover, we suggest that these sponges could be used as scaffolds for growing cells in systems with low mechanical loading in tissue engineering, especially in dermis replacement, where neovascularization is a crucial parameter for successful skin regeneration. Due to their antimicrobial properties, these scaffolds are also highly promising for tissue replacement requiring the prevention of infection.
Publication in Chemistry A European Journal
 24. August 2021
24. August 2021
Publication entitled "Chiral Resolution of Spin-Crossover Active Iron(II) [2x2] Grid Complexes" (authors: N. Suryadevara, A. Pausch, E. Moreno-Pineda, A. Mizuno, J. Bürck, A. Baksi, T. Hochdörffer, I. Šalitroš, A. S. Ulrich, M. M. Kappes, V. Schünemann, W. Klopper, M. Ruben ) has been published in the chemistry journal Chemistry A European Journal.
The article describes the preparation, structural and magnetic properties of two tetranuclear ferrous complexes – optical isomers, which are both showing the spin crossover magnetic bistability. The oustdanding results of this work are based on the controlling of the spin crossover properties by the optical isomerism. A bis-tridentate N-donor ligand has been used for the preparation of both ferrous tetranuclear [2+2] grids, where the used ligand can coordinate in the Lambda or Delta configuration. The magnetic properties investigation revealed that both optical isomers are showing almost identical thermal spin crossover, but they show the differences in the photoinduced spin transition properties.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 23. August 2021
23. August 2021
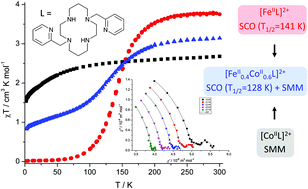
Publication entitled "A multifunctional magnetic material based on a solid solution of Fe(II)/Co(II) complexes with a macrocyclic cyclam-based ligand" (authors: B. Drahoš, I. Šalitroš, I. Císařová, R. Herchel) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In order to prepare a multifunctional magnetic material combining spin crossover together with single-molecular magnetism, co-crystallization of Fe(II) and Co(II) complexes of the pyridine derivative of cyclam (Py2-C = 1,8-bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) was performed. Complexes with the general formula [MII(Py2-C)](ClO4)2·H2O (MII = Fe (1), Co (2) or Fe0.4Co0.6 (3)) were prepared and thoroughly characterized. Based on X-ray molecular structures, they formed octahedral complexes with cis-arrangement of the coordinated pyridine moieties. Magnetic data revealed that the Fe(II) complex 1 shows complete SCO with the transition temperature T1/2 = 141 K, which is preserved also in the mixed Fe/Co system 3 (T1/2 = 128 K). Co(II) complex 2 behaves as a field-induced single-molecule magnet as well as the mixed system 3 with a direct and phonon bottleneck relaxation process, respectively.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 15. July 2021
15. July 2021
Publication entitled " Solvent-induced structural transformation from heptanuclear to decanuclear [Co–Ln] coordination clusters: trapping of unique counteranion and understanding of aggregation pathways" (authors: D. Basak, E. R. Martí, M. Murrie, I. Nemec, D. Ray) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this paper, we report on synthesis and crystal structure of three decanuclear CoII/III-LnIII complexes, which were prepared from heptanuclear precursors by solvent induced aggregation. It was revealed that the aggregation was induced by removal of the methoxido bridging ligands, which were substituted by hydroxido ligands.
Student publication in Dalton Transactions
 15. June 2021
15. June 2021
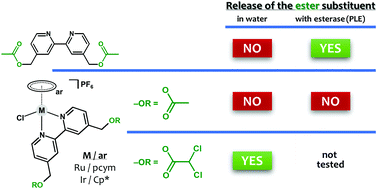
Publication entitled "Unexpected solution behaviour of ester-functionalized half-sandwich Ru(II) and Ir(III) complexes" (authors: L. Masaryk, I. Nemec, J. Kašpárková, V. Brabec, P. Štarha) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this work, we studied the solution behaviour of two half-sandwich Ru(II) and Ir(III) complexes bearing the ester-functionalized 2,2′-bipyridine-based ligand. It was proved that the nature of ester substituent (acetate vs. dichloroacetate) affects the in-solution stability of the ester bond. The experiments performed in the presence of porcine liver esterase (PLE) indicated that although free ester-based ligand was readily metabolized by PLE (acetate release was observed), both complexes containing this ligand were not cleaved by PLE, meaning distinctly different affinity of the used enzyme to the substrate (ligand) when involved in the studied complexes.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 09. June 2021
09. June 2021
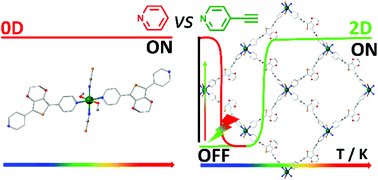
Publication entitled "Thermo- and photoinduced spin state switching in an iron(ii) 2D coordination network associated with large light-induced thermal hysteresis and tuning of dimensionality via ligand modulation" (authors: S. Ghosh, S. Kamilya, T. Pramanik, A. Mohanty, M. Rouzières, R. Herchel, S. Mehta, A. Mondal ) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this work, three Fe(II) coordination compounds were investigated, while by examining the magnetic properties of [Fe(L2)2(NCS)2]n (3) (L2 = 2,5-diethynylpyridinyl-3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene) it was confirmed that the change in spin state is caused by the change in temperature, i.e. it is a spin crossover compound. Photomagnetic experiments confirmed the possibility of switching the spin state even by exposure to light. The study was also supported by theoretical calculations such as DFT, TD-DFT and CASSCF explaining the magnetic and spectroscopic properties of these substances.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 12. May 2021
12. May 2021
Publication entitled "An unexpected in-solution instability of diiodido analogue of picoplatin complicates its biological characterization" (authors: P. Štarha, B. Drahoš, R. Herchel) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this work, we investigated the solution behaviour of biologically prospective complex cis-[PtI2(NH3)(pic)] (pic = 2-methylpyridine), a diiodido analogue of clinically studied Pt-based drug picoplatin (cis-[PtCl2(NH3)(pic)]). We proved both experimentally and theoretically that cis‑[PtI2(NH3)(pic)] is, in contrast to picoplatin, unstable in solution, where it undergoes several processes, including the release of its N-donor pic ligand. This observation complicates the cytotoxicity testing of this Pt(II) diiodido complex.
Student publication in Polyhedron as cover
 31. May 2021
31. May 2021
Publication entitled "Triple M as Manganese: Medicine, magnetism and macrocycles. Seven-coordinate Mn(II) complexes with pyridine-based macrocyclic ligands" (authors: E. Zahradníková, I. Císařová, B. Drahoš) has been published in the chemistry journal Polyhedron. Moreover, the picture describing this work was chosen as a cover artwork for the corresponding issue of the jurnal.
In this work, 3 structurally new ligands L1-L3 derived from a 17-membered macrocyclic ligand with pyridine and piperazine group and their manganese complexes were prepared. Based on the results of X-ray structural analysis, the prepared complexes were found as seven-coordinate with close to the pentagonal bipyramidal geometry. The Mn-Naliphatic bond distances in the equatorial plane were significantly lengthened up to 2.61Å.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 19. April 2021
19. April 2021
Publication entitled "Hydroxido supported and differently networked octanuclear Ni6Ln2 [Ln = GdIII and DyIII] complexes: structural variation, magnetic properties and theoretical insights" (authors: A. Bhanja, L. Smythe, R. Herchel, I. Nemec, M. Murrie, D. Ray) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
In this work, the magnetic properties of two hexanuclear coordination compounds [Gd2Ni6L4(μ3-OH)6(μ-OH)2(CH3CO2)2(μ-H2O)2(H2O)3(MeOH)]·8H2O (1) and [Dy2Ni6L4(μ3-OH)4(μ-Cl)2Cl4(H2O)2(MeOH)2]·2MeOH·4H2O (2) prepared with the same ligand - Schiff base H2L = 2 - {[(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl) imino] methyl} phenol, were investigated. Inspection of the magnetic properties revealed a dominant ferromagnetic exchange interaction in compound 1 and compound 2 was identified as a single molecule magnet. The study was supported by theoretical calculations such as DFT and CASSCF leading to the elucidation of exchange interactions and magnetic anisotropy in these complexes.
Publication in Coordination Chemistry Reviews
 10. February 2021
10. February 2021
Publication entitled "Multinuclear biologically active Ru, Rh, Os and Ir arene complexes" (author: P. Štarha) has been published in the chemistry journal Coordination Chemistry Reviews.
In this review, multinuclear biologically active complexes derived from half-sandwich ruthenium(II), rhodium (III), osmium(II) and iridium(III) arene moieties have been reported. Besides homometallic Ru, Rh, Os and Ir complexes, heterometallic compounds containing the mentioned platinum metals in combination with other d-block elements are discussed as well. Special attention was paid to the comparison of structurally similar analogues differing in the number or type of metal centres.
2020
Publication in Inorganic Chemistry
 15. December 2020
15. December 2020
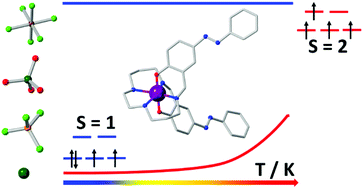
Publication entitled "Reversible Spin-State Switching and Tuning of Nuclearity and Dimensionality via Nonlinear Pseudohalides in Cobalt(II) Complexes" (authors: S. Ghosh, S. Kamilya, M. Rouzières, R. Herchel, S. Mehta, A. Mondal ) has been published in the chemistry journal Inorganic Chemistry.
Herein, we report on investigations of magnetic, spectroscopic and electrochemical properties of two Co(II) coordination compounds with N,N′-di-tert-butyl-2,11-diaza[3,3](2,6)pyridinophane macrocyclic ligand. Complex 1 exhibits a high-spin (S = 3/2) state of cobalt(II) with a large magnetic anisotropy. Interestingly, complex 2 exhibits reversible spin-state switching (T1/2 = 321 K).
Publication in Nanomaterials
 29. October 2020
29. October 2020
Publication entitled "Synergistic Effect of Chitosan and Selenium Nanoparticles on Biodegradation and Antibacterial Properties of Collagenous Scaffolds Designed for Infected Burn Wounds" (authors: J. Dorazilová, J. Muchová, K. Šmerková, S. Kočiová, P. Diviš, P. Kopel, R. Veselý, V. Pavliňáková, V. Adam, L. Vojtová) has been published in the journal Nanomaterials.
A highly porous scaffold is a desirable outcome in the field of tissue engineering. The porous structure mediates water-retaining properties that ensure good nutrient transportation as well as creates a suitable environment for cells. In this study, porous antibacterial collagenous scaffolds containing chitosan and selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) as antibacterial agents were studied. The addition of antibacterial agents increased the application potential of the material for infected and chronic wounds. The morphology, swelling, biodegradation, and antibacterial activity of collagen-based scaffolds were characterized systematically to investigate the overall impact of the antibacterial additives. The additives visibly influenced the morphology, water-retaining properties as well as the stability of the materials in the presence of collagenase enzymes. Even at concentrations as low as 5 ppm of SeNPs, modified polymeric scaffolds showed considerable inhibition activity towards Gram-positive bacterial strains such as Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus and S. epidermidis.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 29. October 2020
29. October 2020
Publication entitled "From solid state to in vitro anticancer activity of copper(II) compounds with electronically-modulated NNO Schiff base ligands" (authors: L. Rigamonti, F. Reginato, E. Ferrari, L. Pigani, L. Gigli, N. Demitri, P. Kopel, B. Tesarova, Z. Heger) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
The copper(II) complexes of general formula [Cu(GL)(Cl)] (1–3, G = OMe, H and NO2, respectively), bearing tridentate Schiff base ligands (GL−) and a chloride as a fourth labile one, are here reported. The Schiff bases derive from the monocondensation of ethylenediamine and substituted salicylaldehyde, where the electronic properties are modulated by the releasing or withdrawing power of the G group. The compounds were structurally characterized through single crystal Synchrotron X-ray diffraction experiments in the solid state. In vitro tests on cell viability were conducted on malignant cell lines. All compounds were capable of formation of intracellular reactive oxygen species and DNA intercalation. This is especially effective for 3 (NO2), which revealed the highest anticancer activity against malignant triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells.
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 10. September 2020
10. September 2020
Publication entitled " Co(ii)-Based single-ion magnets with 1,1′-ferrocenediyl-bis(diphenylphosphine) metalloligands" (authors: J. Hrubý, D. Dvořák, L. Squillantini, M. Mannini, J. van Slageren, R. Herchel, I. Nemec, P. Neugebauer ) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
Herein, we report on investigations of magnetic and spectroscopic properties of three heterobimetallic Fe(II)–Co(II) coordination compounds based on the tetracoordinate {CoP2X2} core encapsulated by dppf metalloligand, where X = Cl (1), Br (2), I (3), dppf = 1,1′-ferrocenediyl -bis(diphenylphosphine). The analysis of static magnetic data has revealed the presence of axial magnetic anisotropy in compounds (1) and (2) and this was further confirmed by high-frequency electron spin resonance (HF-ESR) spectroscopy. Dynamic magnetic data confirmed that (1) and (2) behave as field-induced Single-Ion Magnets (SIMs). Together with bulk studies, we have also tested the possibility of depositing (2) as thick films on Au(111), glass, and polymeric acetate by drop-casting as well as thermal sublimation, a key aspect for the development of future devices embedding these magnetic objects.

Endowment Fund of Palacký University supported our student
 17. july 2020
17. july 2020
Ph.D. student of Inorganic Chemie Mgr. Marie Pražáková received a finantial support from Endowment fung of Palacky University.
Mgr. Marie Pražáková, a first-year doctoral student in Inorganic Chemistry, succeeded and received a financial support from the UP Endowment Fund, which will be very beneficial for solving her research project called Research of Contrast Agents for MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging).
More details can be found on the webpage of the Faculty of Science or UP Endowment Fund.
Congratulations to Marie and we wish her much success in solving the project.

(Mgr. Pražáková second from the right)
Publication in Dalton Transactions
 8. july 2020
8. july 2020
Publication entitled "Late first-row transition metal complexes of a 17-membered piperazine-based macrocyclic ligand: structures and magnetism." (authors: E. Zahradníková, R. Herchel, I. Šalitroš, I. Císařová, B. Drahoš) has been published in the chemistry journal Dalton Transactions.
The 17-membered piperazine-based macrocyclic ligand LdiProp (1,5,13,17,22-pentaazatricyclo[15.2.2.17,11]docosa-7,9,11(22)-triene) was resynthesized in high yield with help of linear pump. Its Mn(II), Fe(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) complexes of general formula [MnLdiProp(ClO4)2] (1), [FeLdiProp(CH3CN)](ClO4)2 (2), [CoLdiProp(CH3CN)](ClO4)2 (3), [NiLdiProp](ClO4)2 (4) were prepared and thoroughly characterized. X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed that Mn(II) complex 1 has capped trigonal prismatic geometry with coordination number seven, Fe(II) and Co(II) complexes 2 and 3 are trigonal prismatic with coordination number six and Ni(II) complex 4 has square pyramidal geometry with coordination number five. The decrease of coordination number is accompanied by a shortening of M–N distances and an increase of torsion of piperazine ring from the equatorial plane. Magnetic measurement reveal moderate for 4 and rather large magnetic anisotropy for 2 and 3 (axial zero-field splitting parameter D(Ni) = 9.0 cm–1, D(Fe) = –14.4 cm–1, D(Co) = –25.8 cm–1, together with rather high rhombicity). Co(II) complex 3 behaves as field-induced SMM with a combination of Raman and direct or Orbach and direct relaxation mechanisms. Obtained magnetic data were extensively supported by theoretical CASSCF calculations. The flexibility and rather large 17-membered macrocyclic cavity of ligand LdiProp could be responsible for the variation of coordination numbers and geometries for investigated late-first row transition metals.